Home Hardening, Fuels Reduction,
Shaded Fuel Breaks
Wildfires pose a serious threat to communities, particularly in areas with dry conditions and abundant vegetation. However, there are several effective strategies homeowners and communities can adopt to reduce the risk of wildfire damage. Three of the most important methods include fuels reduction, home hardening, and the creation of shaded fuel breaks.
What is Fuels Reduction?
Fuels reduction involves the process of managing and reducing the amount of combustible vegetation around your home and community. Wildfires require fuel to spread, and by reducing the available fuel (such as dry leaves, grass, shrubs, and trees), you can slow or stop the spread of a wildfire.
Key Fuels Reduction Strategies:
-
Clearing Dead Vegetation: Remove dry grass, leaves, and dead branches. These materials catch fire easily and can spread a wildfire quickly.
-
Pruning Trees: Trim tree branches at least 6-10 feet above the ground. This reduces the chance of a fire spreading from the ground to the trees.
-
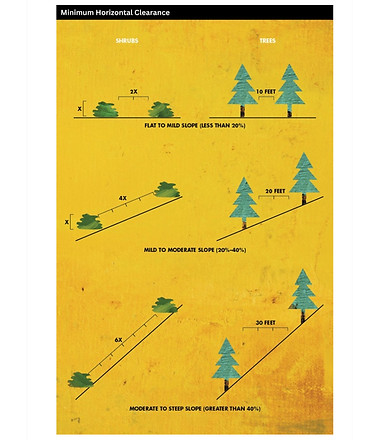
Space Trees and Shrubs: Space out trees and shrubs to create defensible space. Avoid dense clusters of plants that can act as a continuous fuel source for a wildfire.
-
Use Fire-Resistant Landscaping: Replace high-risk plants with fire-resistant alternatives. Consider using gravel or stone as ground cover, which doesn’t catch fire.
Defensible Space per Cal-Fire Zones:
Cal Fire's Defensible Space Zones are designed to create a buffer between your home and the surrounding wildland area to reduce the risk of fire damage. Zone 0 to Zone 3 are the primary areas to focus on in your property for fire safety. Know what

![3[1].jpg](https://static.wixstatic.com/media/84c8a7_b1ae006c85f14c63990dcfecfeaa462b~mv2.jpg/v1/fill/w_199,h_266,al_c,q_80,usm_0.66_1.00_0.01,enc_avif,quality_auto/3%5B1%5D.jpg)

California Regulation Links
Zone 0 (Immediate Zone):
-
Location: Directly around the home, typically within 0 to 5 feet of the structure.
Key Guidelines:
-
Remove all flammable vegetation and materials.
-
Use non-combustible or fire-resistant materials (such as gravel or stone) in this area.
-
Keep mulch, wood piles, and other combustibles away from the home.
-
Trim back any plants or bushes so they don't touch the structure.
-
Ensure there are no trees or shrubs within 10 feet of the chimney or stovepipe.
Zone 1 (Defensible Space Zone):
-
Location: Extends from 5 to 30 feet around the home.
Key Guidelines:
-
Thin out vegetation and trees, ensuring they are well-spaced to reduce the chance of fire spreading.
-
Maintain a defensible space by removing dead or dying plants, leaves, and branches.
-
Trim tree limbs up to 6-10 feet above the ground to prevent fire from climbing up.
-
Consider using fire-resistant plants that are low in fuel content.
Zone 2 (Intermediate Zone):
-
Location: Extends from 30 to 100 feet around the home.
Key Guidelines:
-
Create fuel breaks, including cleared areas, roads, or lawns that can slow or stop a fire's progress.
-
Reduce the density of vegetation by spacing trees at least 10 feet apart, depending on their size.
-
Remove all dead or dry vegetation, and maintain the thinning of trees and shrubs to minimize fire spread.
-
Consider using fire-resistant or low-fuel plants.
Zone 3 (Extended Zone):
-
Location: Beyond 100 feet, this zone includes the larger landscape.


Key Guidelines:
Maintain a defensible space by reducing the potential for fire spread.
This area should be treated as part of the larger landscape management for fire prevention.
These zones are all part of creating a fire-safe environment around your home and improving the ability for firefighters to defend your property in case of a wildfire. The goal is to minimize the fuel available for fire and create defensible space for the structure.
Shaded Fuel Breaks
Shaded fuel breaks are strategically placed areas where vegetation is thinned out, creating a natural barrier to try to slow or stop the spread of a wildfire. These breaks often consist of trees that are spaced out, with the underbrush cleared to create a firebreak.
Benefits of Shaded Fuel Breaks:
Reduced Fire Intensity: By thinning the forest and removing combustible materials, shaded fuel breaks can reduce the intensity of a wildfire, preventing it from spreading rapidly.
Improved Access for Firefighters: Shaded fuel breaks create safer access for firefighting crews and equipment, allowing them to control the fire more efficiently.
Wildlife Habitat Protection: Shaded fuel breaks help protect local wildlife by reducing the severity of wildfires, which can destroy large areas of natural habitat.
Creating Shaded Fuel Breaks:
Selective Tree Removal: Carefully remove trees and brush, especially those that are dead or dying. Ensure that the remaining trees are spaced out and healthy to form a natural firebreak.
Controlled Burns: In some cases, prescribed or controlled burns are used to reduce the undergrowth and vegetation. These are carefully planned and executed by professionals to prevent unintended wildfires.
Regular Maintenance: Keep shaded fuel breaks well-maintained by monitoring the vegetation and removing any new growth that could pose a risk.
How You Can Help: A Community Approach
While individual actions, like home hardening, defensible space, and fuels reduction, are important, communities must work together to reduce wildfire risk. Consider joining or supporting your Fire Safe Council, Prescribed Burn Association, local volunteer fire departments and advocate for fire-safe practices in your neighborhood. Here are some great resources for Northern California communities.
Humboldt County Fire Safe Council
Humboldt Prescribed Burn Association
Trinity County Fire Safe Council
Del Norte Fire Safe Council
Siskiyou Fire Safe Council
Siskiyou Prescribed Burn Association
Modoc Fire Safe Council
Modoc Prescribed Burn Association
Lassen Fire Safe Council
Shasta Fire Safe Council
Shasta Prescribed Burn Association
Final Thoughts
Fuels reduction, defensible space, home hardening, and shaded fuel breaks are all essential components in the fight against wildfires. By taking these steps, homeowners and communities can reduce the risk of property loss, protect valuable natural resources, and safeguard lives. Don’t wait for the fire to come — take action now and ensure your home and community are prepared for the next wildfire season.

.png)

